Litecoin vs Bitcoin: Is ‘Digital Silver’ Good as Gold?

What’s Litecoin and how does it compare to the first cryptocurrency? Why is one called “digital gold” and the other is “digital silver”? Leave it to the ChangeHero team to explain with no fluff.
Key Takeaways
- Litecoin was made as a modified version of Bitcoin but never shared transaction history with it. Bitcoin was launched in early 2009, and Litecoin (LTC) arrived in 2011.
- In comparison to Bitcoin, Litecoin has quicker block times. This change was made to speed up the transaction processing with finality and increase the network’s throughput for daily transactions.
- By all intents and purposes, Bitcoin remains the bigger coin of the two, but Litecoin has carved itself a niche and has a reputation for its longevity.
The Two Crypto Giants
Despite the implications in the name, by now Litecoin is more than just ‘Bitcoin Lite’. Although originally it was a lighter version of Bitcoin, in the big picture today it transcends the comparison and stands well on its own as one of the most well-established altcoins in the space.
What is the exact relationship between Bitcoin and Litecoin? The former was unveiled in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto and launched the next year, laying the foundation for the whole cryptocurrency industry and becoming the template for countless other alternatives, not just Litecoin. Around 2011, when LTC came to be, most commonly, they were built with the Bitcoin code as the foundation. This was also the case for Litecoin, which was developed by Charlie Lee. Unlike hard-forked cryptocurrencies which were spun off from the Bitcoin’s blockchain after changes, separate clients were made for Litecoin and the two chains share no history. When Litecoin is referred to as a “Bitcoin fork”, it means as in software fork, not a hard fork.
Will Litecoin ever be as big as Bitcoin? It does not exactly set out to do so. From the very beginning, Litecoin’s goal was to complement Bitcoin as a digital medium of exchange for daily transactions.
What are Bitcoin and Litecoin?
In case we went ahead of the topic and more clarity is needed, let’s briefly explain both cryptocurrencies in question.
As for the Bitcoin definition, it is the first cryptocurrency which is fully digital and works with the help of a distributed ledger called blockchain. The fact that the records of operations are not tampered with and remain true is ensured by cryptography and consensus of all network participants instead of a centralized entity. Bitcoin was not the first digital currency to be envisioned and developed but it was the first to be launched as a viable network in 2009 by pseudonymous creator(s) Satoshi Nakamoto.
What is LTC crypto currency? As for the Litecoin definition, it is essentially a modified version of Bitcoin that was launched by Charlie Lee in 2011. Modifications included a new mining algorithm, shorter block time of 2.5 minutes and higher supply cap of 84 million LTC. Litecoin was designed to complement Bitcoin for daily transactions with quicker processing and lower fees.
Underlying Technology
Let’s start with the point of comparison that we already mentioned and which will not require lengthy explanations. Fundamentally, both Bitcoin and Litecoin are on their own blockchains and they use Proof-of-Work consensus algorithms. The difference here is in the algorithms and some specifications, so let’s explain those.
SHA-256 vs. Scrypt Algorithms
Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 algorithm to produce hashes that secure the blockchain records. It stands for “Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit” and is famously computationally intensive. Bitcoin’s mining encourages network participants known as “miners” to compete to solve hashes to the next block, so the race for more effective hardware eventually resulted in development of Application-Specific Integrated Circuits, or ASIC miners. These processors are only good for mining Bitcoin but they vastly outperform CPUs and GPUs and incidentally, are more expensive, leading to fewer participants being able to afford mining.
Just two years in, this was already seen as a problem, so Charlie Lee deliberately introduced the Scrypt algorithm to Litecoin. Due to being dependent on RAM rather than raw processing power, GPU mining was more effective for Scrypt, and the algorithm was considered “ASIC-resistant”. That being said, resistant did not mean immune, and eventually, by 2014, Scrypt ASICs entered the markets.
Block Time and Transaction Speed
Another crucial detail that helps Litecoin with its “digital silver” pitch is faster processing times. To see how it’s achieved, we have to explain what block time is.
As the name implies, blockchain is a chain of blocks, so these blocks are added in a sequence in regular intervals. To make sure rising or falling cumulative computational power in the network does not change much how often a new block is added, there is a mechanism called block difficulty. Bitcoin’s mining difficulty calibrates itself so that a new block’s hash is solved and a block is added every 10 minutes on average. Litecoin intended to speed things up fourfold, so the block time was set to 2.5 minutes.
As a result, intended throughput of Litecoin grows to over 50 transactions per second (tps), compared to Bitcoin’s 7 tps. Note the use of “intended” here, as Litecoin’s blockchain rarely is as busy as to process transactions at its full capacity. Rather than a real driver for adoption, higher throughput of Litecoin is more of a nice feature to keep fees lower and blockchain less congested.
So, is Litecoin faster than Bitcoin? After raw transaction speed, there is also finality to consider. A transaction on Bitcoin will be considered securely recorded in 3–6 blocks which take up to 30–60 minutes. Due to Litecoin’s standing and lower hash rate, its finality is slightly bumped up to 10 blocks, which can take up to 25 minutes. Not super fast but still faster than BTC!
Another related modification is a fourfold increase in LTC supply, directly caused by the block time decrease. The Bitcoin protocol specifies there will be no more than 21 million BTC mined, so for Litecoin, the total supply is capped at 84 million LTC. Without going into detail on block rewards and halving, the rate at which the total supply is entering circulation is the same due to Litecoin preserving the original ratio, so supply dynamics are roughly the same for both.
What is Lite coin halving? If you want to get more information about this mechanism, with the Litecoin (LTC) halving history and chart, read our article on the topic!
| Feature | Bitcoin | Litecoin |
| Creator | Satoshi Nakamoto | Charlie Lee |
| Release Date | 2009 | 2011 |
| Hashing Algorithm | SHA-256 | Scrypt |
| Block Time | 10 minutes | 2.5 minutes |
| Total Supply | 21 million BTC | 84 million LTC |
| Mining Reward | 3.125 BTC | 6.25 LTC |
Scalability and Network Fees
Another factor often presented as a Litecoin’s advantage is its lower transaction fees and less network congestion. What Litecoin did to improve scalability from the very start, Bitcoin had to catch up with in subsequent upgrades that introduced SegWit and Lightning Network.
Network Fee Comparison
To use a blockchain, you are expected to add a fee that goes to miners who process your transaction. The fees are not the only but often a deciding factor in how soon your transaction will go through. They are usually calculated based on the size of your transaction: the more inputs it has, the more information has to be processed and more space it will take in the block. While it is not prohibited to up the fee so your transaction gets priority in the queue, the vast majority of users take the economical path and use the minimal feasible amount.
That being said, the BTC fee is calculated in satoshi (the smallest unit of BTC) per byte, and LTC fees use the same formula. At the time of writing, the average fee in the Bitcoin network is 0.0000042 BTC (1.8 sats/vB) versus 0.000047 LTC (0.00000017 LTC/byte), according to Bitinfocharts. In native cryptocurrency, Litecoin’s fees are a bit higher but converted into USD, Bitcoin fees are bound to be more expensive due to BTC being the more expensive digital asset in the comparison. The same average in USD is $0.0056 for LTC versus $0.494 for BTC.
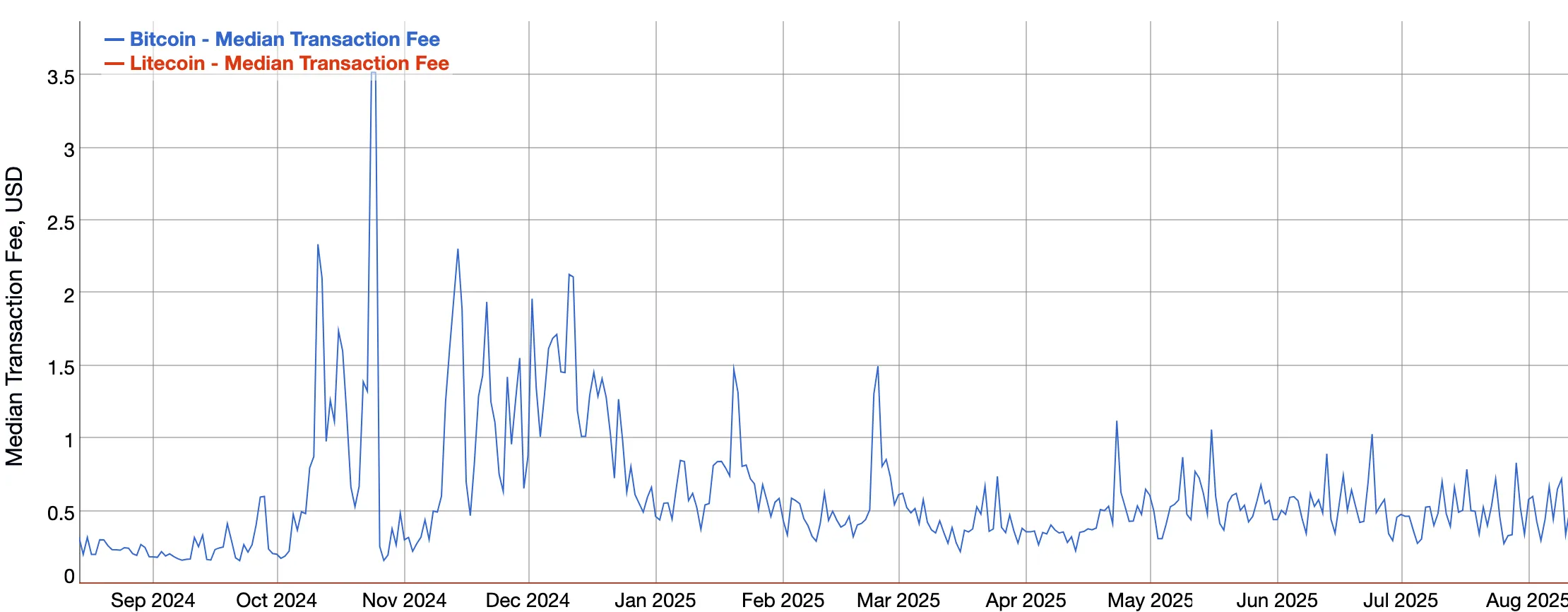
1-year median transaction fee comparison chart for BTC (blue) and LTC (red). Source: Bitinfocharts
On longer time scales, the difference is obvious: when Bitcoin experiences high network load, its fees increase so that the median comes up to $3.5. Litecoin fees, denoted by the red line in the chart above, are close to zero in comparison.
Scalability Challenges and Solutions
Implications of growth were baked into both cryptocurrencies, Litecoin especially. How are they dealing with increasing load?
Fundamental differences aside, the similarity between Bitcoin and Litecoin allow both to share scalability solutions that help with growing the network for more users. One of them is Lightning Network, enabled by the SegWit protocol upgrade. It might surprise you that Litecoin was the first to adopt the Segregated Witness in 2018, serving as a sort of a testing ground for its counterpart.
Lightning Network (LN) is a Layer-2 solution, a network of payment channels that enables low-cost, off-chain transactions where only settlement is recorded on the blockchain.
By then, Bitcoin had already experienced its share of network congestion, which drove the fees to hundreds of dollars and caused transactions to process for days. Integrating Lightning Network was necessary, while in Litecoin, its adoption remained minimal.
Adoption and Market Metrics
To no one’s surprise, when comparing Bitcoin vs. Litecoin, one is evidently perceived as more valuable than the other. Litecoin’s whole proposition saw this arrangement as natural but once you look beyond market valuation into actual adoption rates, things start to look less like they were supposed to be.
Market Capitalization Comparison
In this regard, the numbers do the talking without any need for comment. Bitcoin’s market dominance of the crypto market (in other words, total market share) today is 59.19%, while Litecoin’s is just 0.228%.
More precisely, at the time of writing, the Bitcoin market cap is $2,338,030,379,157 and the Litecoin market cap is $8,999,229,406.6. If we take crypto market capitalization figures to be as reliable as in stocks, then Litecoin would be more valuable than EPAM Systems Inc., American Airlines Group, VinFast Auto Ltd, Levi Strauss Co. and Dropbox Inc. Bitcoin’s valuation is above even more recognizable brands: Meta Platforms Inc., Tesla and JP Morgan Chase.
Adoption and Use Cases
Does that mean that Bitcoin or Litecoin are bigger than these companies respectively? Not necessarily: Bitcoin might be a household name by now but there are still more people using Meta products than BTC. The same could probably be said about Litecoin. In Q2 2025, Dropbox reported 700 million registered users, while the Litecoin blockchain at the very peak (18 Feb 2023) recorded 782 thousand unique active addresses.
Is Litecoin better than Bitcoin at least for what it sets out to do? The Bitcoin adoption as a store of value seems to align with its network metrics but analyzing the Litecoin adoption as a daily payment network, we noticed that BTC still seems to be the choice for more users. Despite quicker payment processing and negligible fees, wider recognition and more solid security make users prefer Bitcoin to Litecoin.
Round-Up of Pros and Cons
Bitcoin’s Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Bitcoin is the most resistant cryptocurrency to consensus attacks and reorganizations thanks to its immense hash rate and the widest global network of nodes.
- BTC has always had a limited supply and scarcity coded into the protocol. The “digital gold” moniker comes from this fact.
- Bitcoin enjoys legitimacy and liquidity that no other cryptocurrency can match yet with its market dominance and widespread recognition.
Cons:
- Low throughput and slow finality make transactions on Bitcoin unfit for a lot of casual scenarios.
- As a consequence of the fee economy coupled with price volatility, network fees are volatile and high demand can drive them to hundreds of dollars per transaction.
- BTC mining in 2025 is a highly competitive business that makes it feasible only on a large scale, reducing the pool of miners and leading to network centralization.
Litecoin: Pros and Cons
Pros:
- In any case, Litecoin’s fees are noticeably lower than Bitcoin.
- Litecoin innovates ahead of Bitcoin, further cementing its role in the crypto industry.
- Higher total supply means that LTC is less under a threat of deflationary spiral and more fit for use as a medium of exchange than BTC.
Cons:
- Compared to other blockchains, Litecoin is adequately secure but pales in comparison to Bitcoin’s security.
- Litecoin lacks the brand recognition and institutional support of Bitcoin, resulting in a much smaller market presence and transaction volume.
- Unlike the pseudonymous and largely unknown creator of Bitcoin, Charlie Lee was a part of controversy when he sold his LTC holdings at a high valuation in late 2017.
| Bitcoin (BTC) | Litecoin (LTC) | |
| Advantages | Unmatched security and decentralization; Established as a store of value; Widest adoption and institutional support; Major innovations like the Lightning Network are being developed to solve scalability issues. | Faster transaction speeds and lower fees; Serves as a testbed for new technologies; Higher on-chain transaction capacity; Lower transaction volume means the network is not congested. |
| Disadvantages | Scalability limitations lead to congestion; High and volatile transaction fees for on-chain transactions; High energy consumption and mining centralization due to ASIC dominance. | Lower network security due to a significantly smaller hashrate; Much lower market capitalization and adoption; The founder's public sale of his holdings may be perceived as a unique point of governance risk. |
Conclusion
Litecoin can hardly be analyzed without bringing Bitcoin into the picture, and since it was designed to complement it, this seems logical and right. Both of these cryptocurrencies have considerable merits that justify their existence in the crypto world.
Did you come here looking to learn more about the distinction or for a comparison between these two currencies? Share your feedback in the comments and read more articles from ChangeHero blog! Subscribe for more content to ChangeHero in Telegram, X (Twitter), and Facebook.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does market capitalization compare between Litecoin and Bitcoin over the last year?
On a yearly scale, Bitcoin has maintained a market capitalization of over $1 trillion, while Litecoin fluctuated between $8 and $10 billion.
Is mining LTC more profitable vs BTC?
Mining profitability depends on hardware, electricity and maintenance costs, as well as many other factors. In vacuum, current Bitcoin ASICs can provide competitive hash rate that will result in profit (unlike Scrypt ASICs) but this fails to account for competition from other miners and the cost of equipment.
What services accept Litecoin but not Bitcoin?
Given that even the Litecoin Foundation recognizes the demand for Bitcoin payments and accepts it along LTC, finding such a service or payment gateway is tricky. Merchants can configure their checkouts to accept LTC without BTC, but their service provider will still be counted as offering both.
How transaction fees differ for Litecoin versus Bitcoin?
Counting in BTC or LTC, Bitcoin’s fees are currently slimmer than Litecoin’s but due to BTC being orders of magnitude more expensive than LTC, Bitcoin fees end up more costly. Bitcoin’s fees are consistently averaging $0.5 while Litecoin takes around $0.005.
Is mining Litecoin more environmentally-friendly versus Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s SHA-256 is more computationally intensive, which has led to the development of ASICs and further increase in energy consumption. Coupled with the demand for Bitcoin specifically, BTC mining results in infamously large carbon footprint and electronic waste. Litecoin, in contrast, uses a more memory-intensive algorithm Scrypt, better suited for more accessible processors. However, lower environmental impact of Litecoin might be the result of its lower market share and demand.





